How to encrypt your data
Encryption or cryptography is a method used to conceal or convert information/data which is sent in an email or stored on (for example) a USB flash drive or computer hard drive.
When data is encrypted, there is a key or a code which explains how data should be encrypted (locked), and how data should be converted back to an intelligible form (unlocked).
Encryption of AU computers
Computers provided after 1 March 2018
If you have an AU computer (Windows or Mac) which was provided to you by your IT support team after 1 March 2018, it is encrypted. This means that all content on the local hard drive is encrypted. An encrypted computer provides far better protection of data, including personal data, if you should be so unfortunate as to lose your computer, for example in case of theft.
Computers provided before 1 March 2018
AU computers (Windows and Mac) provided before 1 March 2018 will be automatically encrypted when the computer is reinstalled.
It is also possible to encrypt an older computer without reinstallation. However, there are some technical requirements for the computer, and you will therefore need to contact your local IT support team if you want to use encryption on an older computer. If the computer does not meet these technical requirements, it may be necessary to replace the computer.
Encrypted USB flash drive/encrypted content on a USB flash drive
AU recommends that you use a USB flash drive with hardware encryption, as these are typically compatible across operating systems.
A hardware-encrypted USB flash drive is somewhat more expensive than a regular USB flash drive with the same capacity, but is often of better quality and has a high level of security, as this type of flash drive often deletes itself after a certain number of incorrect login attempts.
Contact your local IT support team if you have any questions or want to buy an encrypted USB flash drive.
Encrypted content on a regular USB flash drive
You can quickly and easily encrypt content that you need to take with you on a USB flash drive. Once you have encrypted the content, you need a code to access the files.
Should you be so unfortunate as to lose or forget your USB flash drive, the files will remain secret.
Find instructions on how to encrypt content using Bitlocker2Go for Windows.
NB! The USB flash drive cannot be used across PC/Mac/Linux if you choose this option.
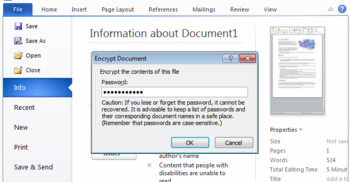
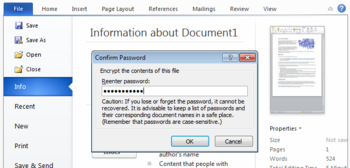
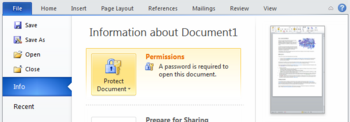
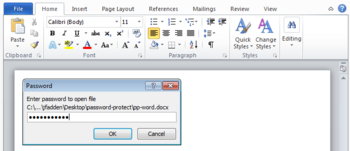
How to encrypt data in Office programs, such as Word and Excel
You can encrypt data in the Office programs using these five steps.
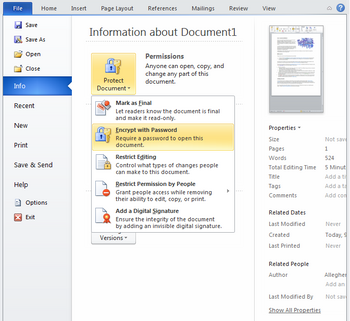
Step 1
Find Encrypt with Password by opening the File menu and selecting Info.
Example of encryption
The following information must be sent from person 1 to person 2 without anyone being able to immediately read and understand this message:
‘The club will meet at 18:00 outside the tower clock’
A key could be that person 1 and person 2 agree that all letters (a-z) in the alphabet must be moved two places, i.e. when you need to write an ‘a’, you write a ‘c’. In the number sequence from 0-9, it can be agreed to move the numbers three places, so when you need to write 1, you write 4.
In other words, both persons have agreed to and know this method for encrypting the message.
Using this key, person 1 must encrypt the original message and structure the information as follows:
‘Vjg enwd yknn oggv cv 41:33 qwvukfg vjg vqygt enqem’
If you do not have the key that has now been agreed between the two persons, it is very difficult to decipher and understand the message, but since both have the key, person 2 can now read it by using the table and the key to translate the message.
In simple terms, this is how encryption works. Computer systems and networks contain highly complex mathematical algorithms for structuring keys that are almost impossible to decipher.